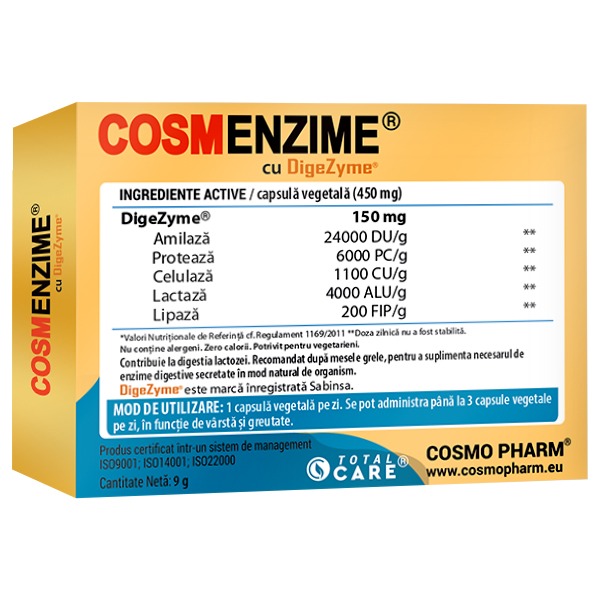
Patented multi-enzyme complex that helps improve digestion, CosmEnzime® with DigeZyme® contains five essential digestive enzymes: amylase, protease, lactase, lipase and cellulase dosed at optimal levels, which work together to break down proteins, carbohydrates and fats into beneficial nutrients, easily absorbed by the body.
Made with high quality ingredients, non-animal origin, tested and approved, being resistant to the action of gastric juices, while maintaining its digestive activity.DigeZyme® has been clinically evaluated for improved absorption of minerals and vitamins (“The Complete Book of Enzyme Therapy” by Anthony J. Chichoke (Ref. 1).
What are digestive enzymes?
Digestive enzymes are protein substances that work to break down the foods we eat into simpler components so that our bodies can absorb and utilize essential nutrients. These enzymes are produced by the digestive glands in the body and are released into the digestive tract, where they act on food.
The Best Natural Digestive Enzymes
There are several natural digestive enzymes that are considered effective and useful for supporting the digestion process and digestive health. Here are some of the best natural digestive enzymes:
- Amylase (α-Amylase 24,000 DU/g): This is found in saliva and the pancreas. When we chew food containing carbohydrates, saliva releases amylase which begins the process of breaking down starch into smaller sugars, such as maltose. Once food reaches the stomach, amylase is inactivated by the acidic environment, but the breakdown process continues in the small intestine, where the pancreas releases amylase to complete the process of converting carbohydrates into absorbable sugars.
DU (Dextrinizing Units) is a unit of measurement for the activity of amylase, the enzyme that breaks down starch and carbohydrates into simpler sugars. Therefore, 24,000 DU/g indicates that each gram of the supplement contains 24,000 units of α-Amylase enzymatic activity.
- Cellulase (Cellulase 1,100 CU/g): is a digestive enzyme that breaks down cellulose, a structural component of the cell walls of plants and other plant sources
Cellulase enzymes play an important role in the digestion of fiber and cellulose, helping to break down these components in food and thus facilitating the release of nutrients and other valuable substances for our body. However, it should be noted that humans produce limited amounts of cellulase, and cellulose in our diet mainly helps maintain intestinal health and stimulate intestinal transit.
CU (Cellulase Units) is a unit of measurement for the activity of cellulase, the enzyme that breaks down fiber and cellulose in plants and other plant sources. 1,100 CU/g indicates that each gram of the supplement contains 1,100 units of Cellulase enzymatic activity.
- Lactase (Lactase 4,000 ALU/g): Lactase is an enzyme that breaks down lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products, into two simpler sugars: glucose and galactose. This process occurs in the small intestine and allows these sugars to be absorbed efficiently into the bloodstream. A person with lactase deficiency does not produce enough lactase to break down lactose, which leads to lactose intolerance and can cause unpleasant digestive symptoms such as bloating, abdominal cramps, flatulence, and diarrhea after consuming lactose.
Lactase supplements can be helpful for people with lactose intolerance because they help break down lactose and can reduce or prevent digestive symptoms associated with consuming lactose.
ALU (Lactase Units Acid Lactase Units) is a unit of measurement for the activity of lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose (milk sugar) into glucose and galactose. Thus, 4,000 ALU/g indicates that each gram of the supplement contains 4,000 units of Lactase enzymatic activity.
- Protease (Neutral protease 6,000 PC/g): these natural digestive enzymes are responsible for breaking down proteins into peptides and amino acids. Proteases are produced mainly in the stomach and pancreascreas, and are essential for the digestion of proteins in food. Proteases also play an important role in the release of nutrients and amino acids necessary for optimal body function.
Protease supplements can be used to support protein digestion and ensure more efficient absorption of amino acids. These supplements may be beneficial for people with digestive disorders or during periods of difficult digestion, such as after high-protein meals.
PC (Protease Units) is a unit of measurement for the activity of neutral proteases, enzymes that break down proteins into peptides and amino acids in a neutral environment. 6,000 PC/g indicates that each gram of the supplement contains 6,000 units of Neutral Protease enzyme activity.
- Lipase (Lipase 200 FIP/g): is produced primarily in the pancreas and is released into the small intestine when we consume fatty foods. It acts on fats as they move through the intestine, breaking them down into smaller substances that can be absorbed and metabolized.
FIP (Federation Internationale Pharmaceutique) is a unit of measurement for the activity of lipase, the enzyme that breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. 200 FIP/g indicates that each gram of the supplement contains 200 units of Lipase enzyme activity.
These are types of natural digestive enzymes included in supplements to support the digestion process and facilitate the efficient breakdown of nutrients in food.
Digestive Enzyme Deficiency
Digestive Enzyme Deficiency, also known as enzyme insufficiency, is a condition in which the body does not produce enough digestive enzymes or in which the activity of the enzymes is reduced, leading to incomplete digestion of nutrients in food. This can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms and affect health. It can also lead to nutritional deficiencies, as the body cannot absorb enough nutrients from food.
People prone to digestive enzyme deficiency include:
- People with pancreatic disorders: The pancreas is a gland that produces a number of digestive enzymes, including lipase, protease, and amylase. Pancreatic disorders, such as pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) or cystic fibrosis (a genetic disease that affects the pancreas and other organs), can lead to an enzyme deficiency and impaired digestion.
- Genetic factors: Some people may have genetic conditions or mutations that affect the production or function of digestive enzymes, leading to enzyme deficiencies.
- Nutrient deficiencies: Insufficient intake of essential nutrients, especially those involved in the production or function of enzymes, can contribute to digestive enzyme deficiencies.
- Intestinal infections or inflammation: Infections or inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract can disrupt the production and activity of digestive enzymes, affecting digestion.
- Undetected celiac disease: Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition in which eating gluten causes damage to the small intestine. This can lead to decreased enzyme production and absorption problems.
- Physical, emotional, or psychological stress: Stress can affect the digestive system, affecting enzyme secretion and digestion.
- Smoking: Smoking can negatively affect the digestive system and reduce enzyme activity.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can alter digestive enzyme levels and affect digestion.
- Aging: As we age, there may be a natural decrease in digestive enzyme production, which can lead to reduced digestive capacity.
- People with food intolerances: Certain food intolerances can be caused by a deficiency in digestive enzymes. For example, lactose intolerance is the result of a deficiency of lactase, the enzyme responsible for breaking down lactose (milk sugar). In the case of gluten intolerance, which is a protein found in wheat, barley and rye, a deficiency of protease enzymes can contribute to difficulties digesting gluten.
- Somatic diseases that require treatment with surgical procedures, antibiotics and immunosuppressive drugs.
Restoring digestive enzymes
Restoring digestive enzymes naturally can be achieved by adopting healthy eating and lifestyle habitsHere are some tips to help support the regeneration of digestive enzymes:
- Eat a balanced diet: Make sure your diet contains a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals for the optimal production and functioning of digestive enzymes.
- Chew your food well, this process also facilitates the functioning of digestive enzymes in the intestines.
- Limit the consumption of processed foods and fast food, they may contain chemical additives that can affect the production of digestive enzymes.
- Include fermented foods in your diet, such as probiotic yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut or pickles – they contain beneficial bacteria that can help improve digestion and intestinal health.
- Reduce alcohol consumption and smoking which can negatively affect digestive health and the production of digestive enzymes.
- Adequate water consumption facilitates the movement of food through the digestive tract and can support the functioning of digestive enzymes.
- Chronic stress can affect the digestive system and secretion enzymatic, therefore, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises can help manage stress and promote healthy digestion.
- Regular physical activity: Regular physical exercise can stimulate the digestive system and improve blood circulation to the digestive organs, thus supporting the activity of digestive enzymes.
Food intolerance
Food intolerances and lack of digestive enzymes are two problems related to digestion that can cause unpleasant digestive symptoms.
Food intolerance is the inability of the body to digest or tolerate certain foods. It does not involve an immune system response, as is the case with food allergies. Instead, it is caused by the lack or insufficiency of certain digestive enzymes necessary for the complete breakdown of certain food components.
Common examples of food intolerances include:
Lactose intolerance: caused by a deficiency of lactase, the enzyme that breaks down lactose (milk sugar) into glucose and galactose. A lack of lactase can cause symptoms such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, or cramps after consuming dairy products.
Gluten intolerance: In those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, consuming gluten (a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye) can cause inflammation in the small intestine and disrupt nutrient absorption.
Other intolerances: People can be intolerant to various food components, such as histamine, fructose or sorbitol, and the lack of appropriate digestive enzymes can be a cause in these situations.
Symptoms of digestive enzyme deficiency:
Symptoms of digestive enzyme deficiency can vary depending on the type and severity of the enzyme deficiency, as well as the foods consumed. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Excessive bloating and gas;
- Abdominal discomfort and cramps;
- Diarrhea or frequent bowel movements;
- Constipation;
- Feeling full in the stomach after small meals;
- Low or insufficient body weight;
- Nutritional deficiencies, due to improper absorption of nutrients from food.
Benefits of digestive enzymes:
- Contribute to efficient digestion;
- Reduce unpleasant digestive symptoms;
- Amylase contributes to the breakdown of starch and carbohydrates;
- Helps reduce bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort, diarrhea or constipation, especially in people with food intolerances or enzyme deficiencies;
- Contributes to maintaining gut health and intestinal barrier function;
- Helps reduce inflammation associated with digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome or gastroesophageal reflux;
- Contributes to protection against inflammation and increased intestinal permeability;
- Contributes to the proper breakdown of food;
- Supports the body to more easily absorb nutrients, especially glucose;
- Contributes to the digestion of fiber and cellulose, aiding digestion in case of food intolerance;
- Contributes to the reduction of digestive symptoms associated with lactose intolerance;
- Supports the digestion of proteins and ensures more efficient absorption of amino acids;
- Contributes to ease digestion in people with digestive disorders or after meals rich in protein;
- Lipase supports the breakdown of fats into fatty acids and glycerol;
- Contributes to the optimal absorption of essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals and amino acids;
- Supports the chemical reactions necessary for cellular functions;
- Restores the natural production of digestive enzymes in people with age;
- Supports the reduction of the body’s effort to break down food;
- Contributes to maintaining energy and vitality;
- Helps reduce oxidative stress;
- Contributes to optimal functioning of the immune system;
- Supports restful sleep after a hearty dinner;
- Benefits for delayed onset muscle pain and other activities related to good digestion:
- Supports improved mental capacity;
- Helps reduce excess weight and fat;
- Contributes to preventing aging skin.
Contraindications:
There are some important contraindications when it comes to using digestive enzymes or enzyme supplements.
- Active gastric or duodenal ulcer, as digestive enzymes may stimulate gastric acid secretion and worsen symptoms in the case of an active gastric or duodenal ulcer.
- People with severe pancreatic disease (chronic pancreatitis, advanced pancreatic insufficiency) should consult a doctor before using a natural digestive enzyme supplement.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should talk to their doctor before starting to use digestive enzymes to assess their safety during this period.
- Some digestive enzymes may interact with certain medications. Before starting a treatment with enzyme supplements, inform your doctor about any other medication or supplement you are taking to prevent unwanted interactions.
Composition
Nutritional information/ 1 vegetable capsule (450 mg):
| DigeZyme® | 150 mg |
|---|---|
| Containing: | 24000 DU/g |
| Amylase | 6000 PC/g |
| Protease | 1100 CU/g |
| Cellulase | 4000 ALU/g |
| Lactase | 200 FIP/g |
| Lipaza | 24000 DU/g |
*Allergen-free. Titanium dioxide-free. Suitable for vegetarians.
DOSE: 1 vegetable capsule per day.
Take 1 capsule per day.
Indicated in:
- Bloating or feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- Gas and excessive flatulence;
- Heartburn or gastric reflux;
- Feeling of nausea or vomiting;
- Abdominal pain or discomfort after eating;
- After foods with a higher fat content;
- In food intolerances;
- In a high-protein, low-carb (e.g. Dukan) or vegan diet.
Can be combined with:
- Constipation – HERBOLAX® NEW FORMULA; HERBOLAX + CRUSIN; HERBOLAX®
- Gas/flatulence – Bio CARBONOX ACTIVE DETOX® COMPLEX
- Digestive health and balance of intestinal flora: Probiotic Complex
- Improving intestinal transit and colon health: COLONOX COLON DETOX®
- To increase the absorption of vitamins and minerals: GERIATRIC VITA-MIN, ESSENTIAL VITA-MIN, MULTIVITAMINS MULTIMINERALS.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.