Cele mai cumpărate
FIER + VITAMINA C DUO LIPOZOMAL
101.64 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 101.64 lei.91.48 leiPrețul curent este: 91.48 lei.Magneziu Lipozomal pentru absorbtie maxima
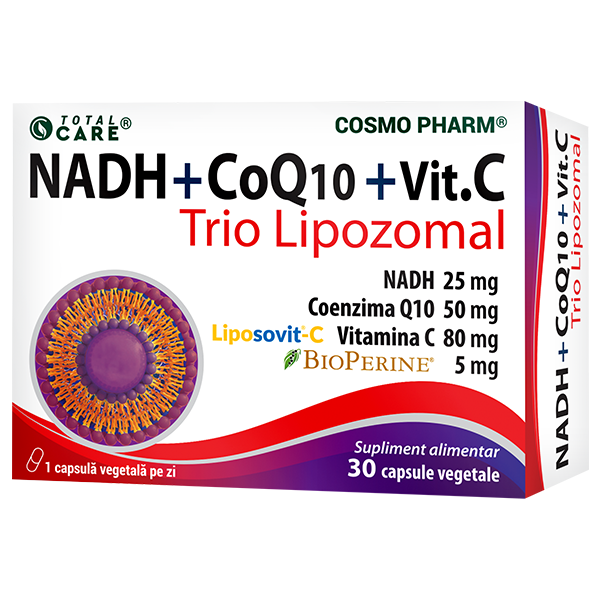
86.52 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 86.52 lei.77.87 leiPrețul curent este: 77.87 lei.NADH + COENZIMA Q10 + VITAMINA C – Trio Lipozomal
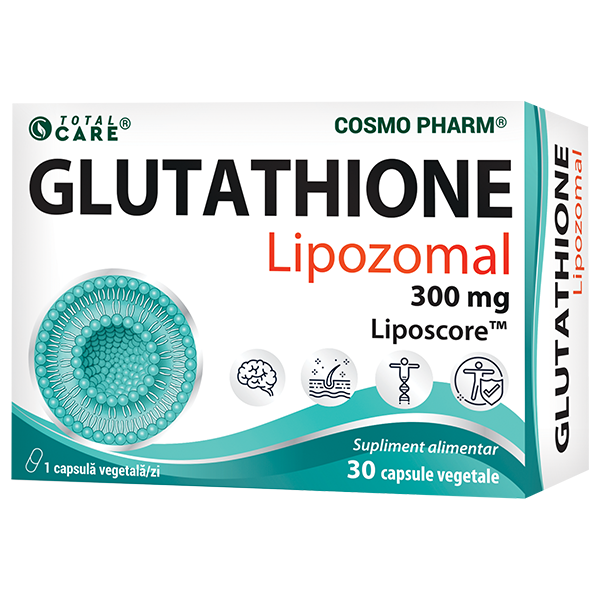
118.58 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 118.58 lei.83.01 leiPrețul curent este: 83.01 lei.GLUTATHIONE LIPOZOMAL 300 mg
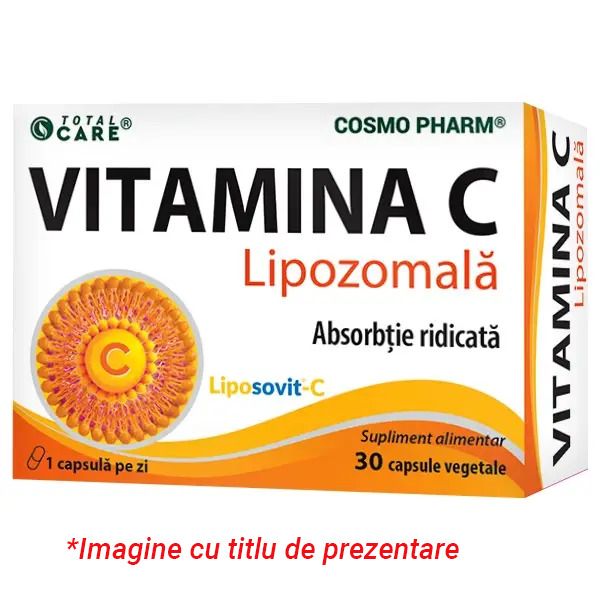
119.79 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 119.79 lei.107.81 leiPrețul curent este: 107.81 lei.Vitamina C Lipozomala Liposovit-C – pana la 1000 mg administrare zilnica
100.43 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 100.43 lei.90.39 leiPrețul curent este: 90.39 lei.Vitamina D3 K2 Lipozomala – absorbtie ridicata
59.90 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 59.90 lei.41.93 leiPrețul curent este: 41.93 lei.COENZIMA Q10 Lipozomală
120.40 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 120.40 lei.108.36 leiPrețul curent este: 108.36 lei.Renox® Renal Detox 30 cps. Detoxifiant, Diuretic
54.39 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 54.39 lei.38.07 leiPrețul curent este: 38.07 lei.PACHET Picioare usoare – Circulatie periferica, retentie de apa
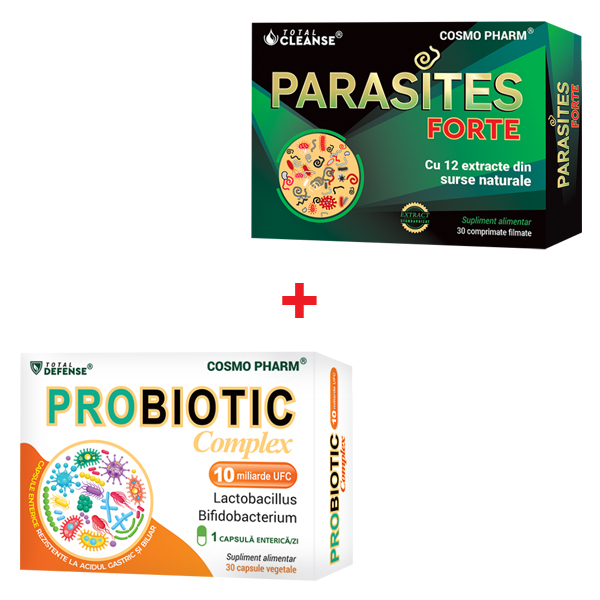
114.33 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 114.33 lei.80.03 leiPrețul curent este: 80.03 lei.Pachet PARASITE CLEANSE
101.57 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 101.57 lei.76.18 leiPrețul curent este: 76.18 lei.PACHET LAX & CLEANSE – LAXATIV NATURAL SI DETOX COLON
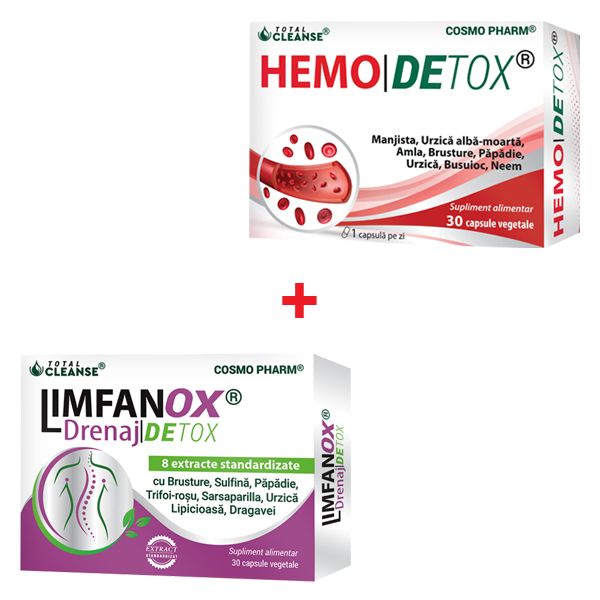
93.80 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 93.80 lei.65.66 leiPrețul curent este: 65.66 lei.Pachet DETOX TOTAL
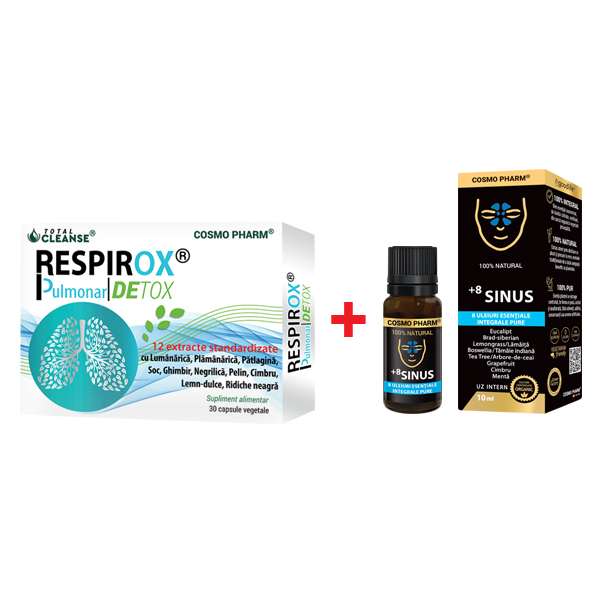
96.57 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 96.57 lei.72.43 leiPrețul curent este: 72.43 lei.Pachet AirFree
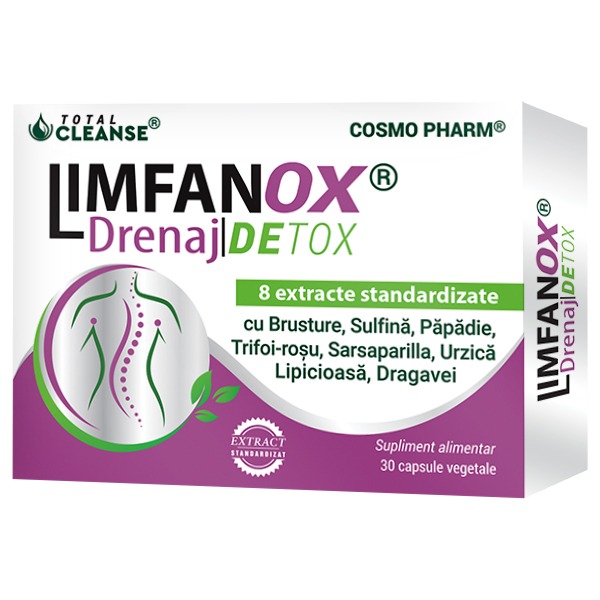
104.90 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 104.90 lei.78.67 leiPrețul curent este: 78.67 lei.LIMFANOX Drenaj DETOX® Capsule Drenaj Sistem Limfatic
57.72 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 57.72 lei.40.40 leiPrețul curent este: 40.40 lei.HERBOLAX® NEW FORMULA*
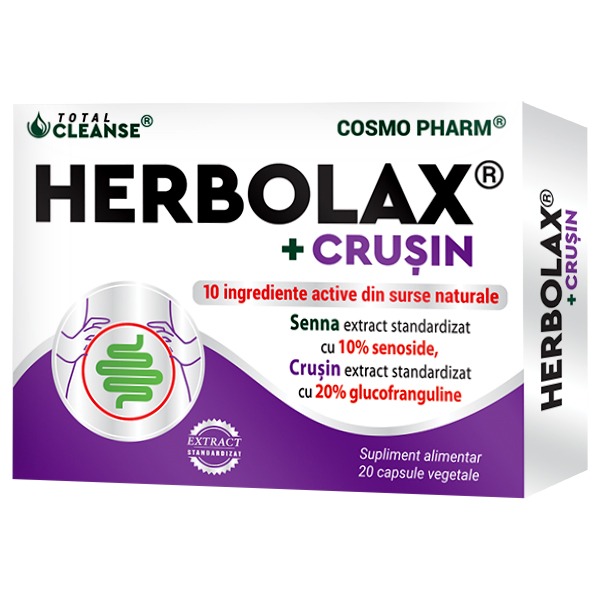
28.31 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 28.31 lei.19.82 leiPrețul curent este: 19.82 lei.HERBOLAX® + CRUSIN Laxativ Natural Pentru Constipatie Cronica
31.64 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 31.64 lei.22.15 leiPrețul curent este: 22.15 lei.HERBOLAX, laxativ natural, 10 / 30 tablete
32.75 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 32.75 lei.22.92 leiPrețul curent este: 22.92 lei.GLUTATHIONE LIPOZOMAL 300 mg
119.79 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 119.79 lei.107.81 leiPrețul curent este: 107.81 lei.Promoții
Zinc Bisglicinat (chelat) 25 mg biodisponibilitate ridicata
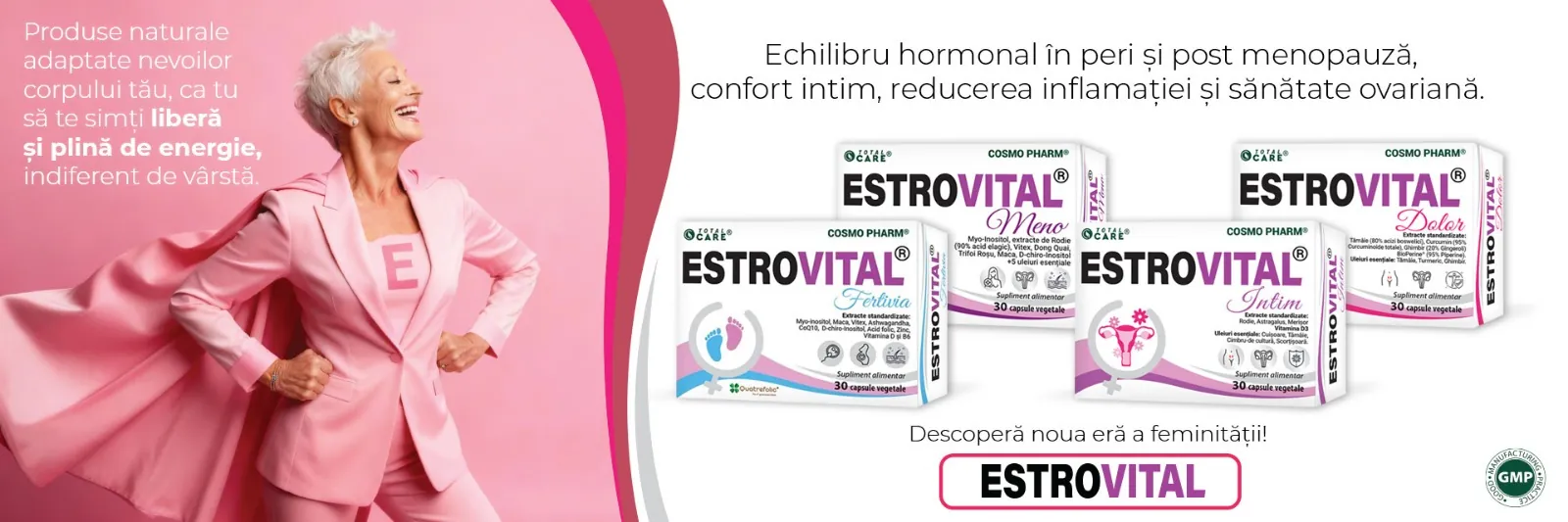
32.07 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 32.07 lei.22.40 leiPrețul curent este: 22.40 lei.Vitex 800 – Supliment Menopauza – Premenopauza
24.42 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 24.42 lei.17.09 leiPrețul curent este: 17.09 lei.VITAMINA E Naturala D-alpha Tocoferol Capsule
64.94 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 64.94 lei.45.46 leiPrețul curent este: 45.46 lei.Vitamina D3 K2 Lipozomala – absorbtie ridicata
59.90 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 59.90 lei.41.93 leiPrețul curent este: 41.93 lei.VITAMINA D3 5000 UI
27.10 lei – 44.04 leiInterval de prețuri: 27.10 lei până la 44.04 leiVitamina D3 2000 UI + K2 (MK-7)
29.22 lei – 52.51 leiInterval de prețuri: 29.22 lei până la 52.51 leiTransport gratuit
la comenzi de peste 150 leiOferte zilnice
cu reduceri până la 30%Retur gratuit
în 30 de zilePlătește în siguranță
on-line cu card bancarBonus special
pentru abonații la newsletterNou în portofoliu
Alga AFA COMPLEX • Chlorella • Spirulina – complex premium 3-în-1 cu microalge
51.28 lei – 93.24 leiInterval de prețuri: 51.28 lei până la 93.24 leiVITAMINA D3 5000 UI
27.10 lei – 44.04 leiInterval de prețuri: 27.10 lei până la 44.04 leiVitamina D3 2000 UI + K2 (MK-7)
29.22 lei – 52.51 leiInterval de prețuri: 29.22 lei până la 52.51 leiMEGABIOTIC® FEMINA 20 Miliarde de Prieteni într-o capsula
45.98 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 45.98 lei.32.19 leiPrețul curent este: 32.19 lei.Vitamina D3 K2 Lipozomala – absorbtie ridicata
59.90 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 59.90 lei.41.93 leiPrețul curent este: 41.93 lei.Sari la conținutVITAMINA D3 5000 UI
27.10 lei – 44.04 leiInterval de prețuri: 27.10 lei până la 44.04 leiVitamina D3 2000 UI + K2 (MK-7)
29.22 lei – 52.51 leiInterval de prețuri: 29.22 lei până la 52.51 leiVitamina C Lipozomala Liposovit-C – pana la 1000 mg administrare zilnica
100.43 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 100.43 lei.90.39 leiPrețul curent este: 90.39 lei.TRIO ANTIOXIDANT DETOX
98.50 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 98.50 lei.73.87 leiPrețul curent este: 73.87 lei.SLIM CONTROL – Concentrat cu Oțet de mere
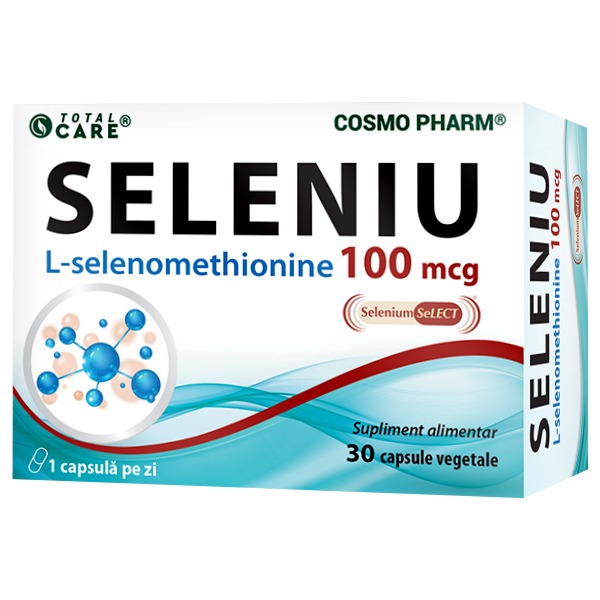
43.29 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 43.29 lei.30.30 leiPrețul curent este: 30.30 lei.SELENIUM SELECT®
25.41 leiPrețul inițial a fost: 25.41 lei.17.79 leiPrețul curent este: 17.79 lei.COSMO PHARM ESTE SPONSOR PRINCIPAL GAUDEAMUS COSMO PHARM SUSTINE OLIMPICII DE AUR AI ROMANIEI![Acasă]()
De ce să alegi
COSMO PHARM![Acasă]() Formule cu biodisponibilitatea maximă, pentru efecte cât mai rapide, cu doar 1-2 capsule pe zi.
Formule cu biodisponibilitatea maximă, pentru efecte cât mai rapide, cu doar 1-2 capsule pe zi.![Acasă]() Extracte standardizate care garantează aceeași eficiență a produsului indiferent de loc.
Extracte standardizate care garantează aceeași eficiență a produsului indiferent de loc.![Acasă]() Ingrediente din culturi certificate organic, de la cei mai mari producători mondiali de materie primă din domeniu.
Ingrediente din culturi certificate organic, de la cei mai mari producători mondiali de materie primă din domeniu.![Acasă]() Suplimente alimentare dezvoltate în laborator de cercetare la cele mai avansate standarde în domeniu.
Suplimente alimentare dezvoltate în laborator de cercetare la cele mai avansate standarde în domeniu.![Acasă]() Produse potrivite pentru vegetarieni, fără alergeni, conservanți, coloranți, arome artificiale, zahăr, sodiu, grău/gluten, ouă și lactate.
Produse potrivite pentru vegetarieni, fără alergeni, conservanți, coloranți, arome artificiale, zahăr, sodiu, grău/gluten, ouă și lactate.![Acasă]() Unitate de producție complet auto sustenabilă, prietenoasă cu mediul înconjurător si ambalaje din materiale reciclabile.
Unitate de producție complet auto sustenabilă, prietenoasă cu mediul înconjurător si ambalaje din materiale reciclabile.Sfatul specialistului
![Acasă]()
![Acasă]()
ABONEAZĂ-TE LA NEWSLETTER
ȘI PRIMEȘTI INSTANT10% DISCOUNT*
* Reducerea se poate cumula cu alte oferte.
![Acasă]()